关于musl libc的资料比赛期间找到过一篇从一次 CTF 出题谈 musl libc 堆漏洞利用,碍于musl libc在1.2.x之后的堆管理机制有较大的改版,因而有了该文章。本次文章分上下两篇,从musl libc 1.2.2的源码审计、调试,以及其中的利用机会,再到mooosl这道题的解题过程做一个分析。
musl libc 1.2.2的源码可以从[此处],(https://musl.libc.org/releases/musl-1.2.2.tar.gz)下载获得。1.2.x采用src/malloc/mallocng内的代码,其堆管理结构与早期版本几乎完全不同,而早期的堆管理器则放入了src/malloc/oldmalloc中。
调试带符号的musl libc
0x01源码编译
题目提供的libc.so不带符号,很难通过调试去理解musl堆管理器的数据结构,可以通过源码编译,生成一份带调试符号的libc.so,进行源码级debug。
tar -xzvf ./musl-1.2.2.tar.gz cd musl-1.2.2 mkdir build x64 cd build CC="gcc" CXX="g++" \ CFLAGS="-g -g3 -ggdb -gdwarf-4 -Og -Wno-error -fno-stack-protector" \ CXXFLAGS="-g -g3 -ggdb -gdwarf-4 -Og -Wno-error -fno-stack-protector" \ ../configure --prefix=/home/sung3r/workspace/sharefd/glibc/glibc-2.32/x64 --disable-werror make make install
在/src/x64/下找到编译好的libc.so
通过patchelf将ld.so改成libc.so即可,gdb调试时加上dir /path/to/musl-1.2.2/src/malloc/和dir /path/to/musl-1.2.2/src/malloc/mallocng便可源码调试。
0x02安装调试符号
此方法要在ubuntu 20.04下才能成功
下载musl_1.2.2-1_amd64.deb、musl-dbgsym_1.2.2-1_amd64.ddeb
在ubuntu20.04安装
sudo dpkg -i musl_1.2.2-1_amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i musl-dbgsym_1.2.2-1_amd64.ddeb
gdb调试时通过dir加载源码即可。推荐此方法,比较简单,而且该deb里的libc.so与题目提供的libc.so md5一致。
源码审计
meta.h
//line:124~127 static inline int get_slot_index(const unsigned char *p) { //chunk地址往前的第3个byte就是该chunk的下标 return p[-3] & 31; } //line:129~157 static inline struct meta *get_meta(const unsigned char *p) { assert(!((uintptr_t)p & 15));//16字节对齐 //获取slot的偏移offset,offset*0x10才是真实偏移 int offset = *(const uint16_t *)(p - 2); //获取slot的下标,这里的slot就是我们习惯中理解的chunk int index = get_slot_index(p); if (p[-4]) { //如果offset不为0,表示不是group里的首个chunk,抛出异常 assert(!offset); offset = *(uint32_t *)(p - 8); assert(offset > 0xffff); } //获取group首地址,也即`meta->mem`这个地址 const struct group *base = (const void *)(p - UNIT*offset - UNIT); //获取meta地址,group首地址指向meta结构的地址 const struct meta *meta = base->meta; assert(meta->mem == base); assert(index <= meta->last_idx); assert(!(meta->avail_mask & (1u< assert(!(meta->freed_mask & (1u< const struct meta_area *area = (void *)((uintptr_t)meta & -4096); //校验Page的secret是否正确,防止伪造Page assert(area->check == ctx.secret); if (meta->sizeclass < 48) {//一般都为48个sizeclass assert(offset >= size_classes[meta->sizeclass]*index); assert(offset < size_classes[meta->sizeclass]*(index+1)); } else { assert(meta->sizeclass == 63); } if (meta->maplen) { assert(offset <= meta->maplen*4096UL/UNIT - 1); } return (struct meta *)meta; } //line:229~238 //16字节对齐向上取整,最后换算成size_classes的下标,对group进行分类 static inline int size_to_class(size_t n) { n = (n+IB-1)>>4; if (n<10) return n; n++; int i = (28-a_clz_32(n))*4 + 8; if (n>size_classes[i+1]) i+=2; if (n>size_classes[i]) i++; return i; } mallocng/malloc.c:
//line:174~284 static struct meta *alloc_group(int sc, size_t req) { ... } else {///通过brk分配 int j = size_to_class(UNIT+cnt*size-IB); int idx = alloc_slot(j, UNIT+cnt*size-IB); if (idx < 0) { free_meta(m); return 0; } struct meta *g = ctx.active[j]; p = enframe(g, idx, UNIT*size_classes[j]-IB, ctx.mmap_counter); m->maplen = 0; p[-3] = (p[-3]&31) | (6<<5); for (int i=0; i<=cnt; i++) p[UNIT+i*size-4] = 0;///根据size清零mem active_idx = cnt-1; } ... } //line:300~381 //malloc的实现,lite_malloc调这里 void *malloc(size_t n) { if (size_overflows(n)) return 0; struct meta *g; uint32_t mask, first; int sc; int idx; int ctr; //大于某一个阈值,通过mmap分配 if (n >= MMAP_THRESHOLD) {///p MMAP_THRESHOLD; $10 = 0x1ffec size_t needed = n + IB + UNIT; void *p = mmap(0, needed, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANON, -1, 0); if (p==MAP_FAILED) return 0; wrlock(); step_seq(); g = alloc_meta(); if (!g) { unlock(); munmap(p, needed); return 0; } g->mem = p; g->mem->meta = g; g->last_idx = 0; g->freeable = 1; g->sizeclass = 63; g->maplen = (needed+4095)/4096; g->avail_mask = g->freed_mask = 0; // use a global counter to cycle offset in // individually-mmapped allocations. ctx.mmap_counter++; idx = 0; goto success; } //否则通过brk分配 //根据传入size,转换成size_classes的下标,根据sc申请相对应group的chunk sc = size_to_class(n); rdlock(); //根据sc,获取存放着对应size group的meta,如果还没申请过这类group,对应ctx.active[sc]为0 g = ctx.active[sc]; // use coarse size classes initially when there are not yet // any groups of desired size. this allows counts of 2 or 3 // to be allocated at first rather than having to start with // 7 or 5, the min counts for even size classes. if (!g && sc>=4 && sc<32 && sc!=6 && !(sc&1) && !ctx.usage_by_class[sc]) { size_t usage = ctx.usage_by_class[sc|1]; // if a new group may be allocated, count it toward // usage in deciding if we can use coarse class. if (!ctx.active[sc|1] || (!ctx.active[sc|1]->avail_mask && !ctx.active[sc|1]->freed_mask)) usage += 3; if (usage <= 12) sc |= 1; g = ctx.active[sc]; } for (;;) { mask = g ? g->avail_mask : 0; first = mask&-mask; if (!first) break; if (RDLOCK_IS_EXCLUSIVE || !MT) g->avail_mask = mask-first; else if (a_cas(&g->avail_mask, mask, mask-first)!=mask) continue; idx = a_ctz_32(first); goto success; } upgradelock(); //申请分配sc类别的chunk,size为n idx = alloc_slot(sc, n); if (idx < 0) { unlock(); return 0; } g = ctx.active[sc]; success: ctr = ctx.mmap_counter; unlock(); return enframe(g, idx, n, ctr); } //line:286~298 //申请chunk static int alloc_slot(int sc, size_t req) { uint32_t first = try_avail(&ctx.active[sc]); if (first) return a_ctz_32(first); //申请group,group信息存放于meta结构 struct meta *g = alloc_group(sc, req); if (!g) return -1; g->avail_mask--; queue(&ctx.acti ve[sc], g); return 0; } free.c
//line:101~143 void free(void *p) { if (!p) return;//地址为0,直接返回 //获取meta结构,以及做一些检查 struct meta *g = get_meta(p); //获取chunk的下标 int idx = get_slot_index(p); size_t stride = get_stride(g); unsigned char *start = g->mem->storage + stride*idx; unsigned char *end = start + stride - IB; get_nominal_size(p, end); uint32_t self = 1u<2u<last_idx)-1; //将对应chunk的下标置0xff ((unsigned char *)p)[-3] = 255; // invalidate offset to group header, and cycle offset of // used region within slot if current offset is zero. //将chunk的offset清0 *(uint16_t *)((char *)p-2) = 0; // release any whole pages contained in the slot to be freed // unless it's a single-slot group that will be unmapped. if (((uintptr_t)(start-1) ^ (uintptr_t)end) >= 2*PGSZ && g->last_idx) { unsigned char *base = start + (-(uintptr_t)start & (PGSZ-1)); size_t len = (end-base) & -PGSZ; if (len) madvise(base, len, MADV_FREE); } // atomic free without locking if this is neither first or last slot //设置meta的avail_mask`freed_mask for (;;) { uint32_t freed = g->freed_mask; uint32_t avail = g->avail_mask; uint32_t mask = freed | avail; assert(!(mask&self)); if (!freed || mask+self==all) break; if (!MT) g->freed_mask = freed+self; else if (a_cas(&g->freed_mask, freed, freed+self)!=freed) continue; return; } wrlock(); struct mapinfo mi = nontrivial_free(g, idx); unlock(); if (mi.len) munmap(mi.base, mi.len); } meta、group、chunk的具体结构,以下通过debug进行分析。
分配释放
store('a0a0', 'b0b0') store('a1a11', 'b1b1111') delete('a0a0') __malloc_context是musl libc的全局管理结构指针,存放在libc.so的bss段
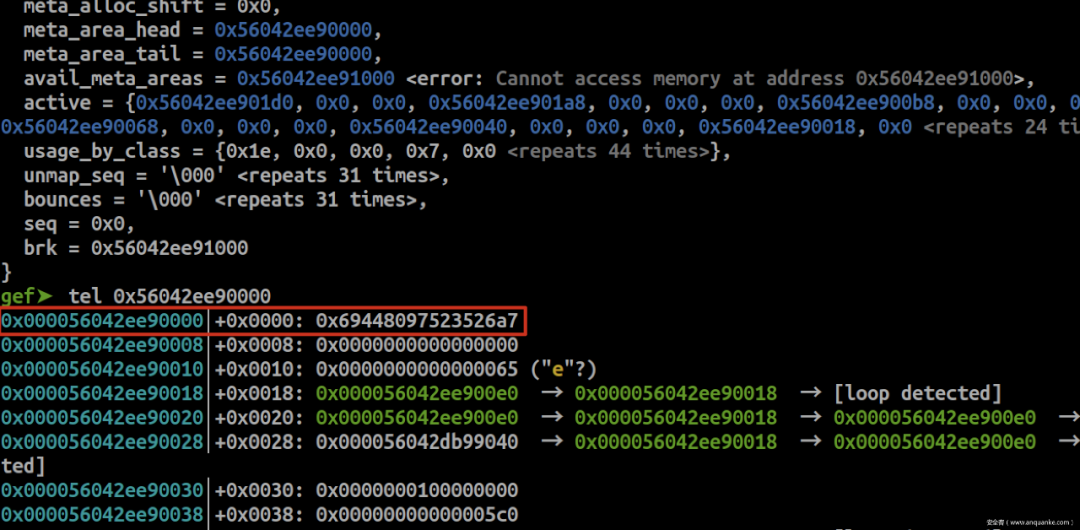
gef➤ p __malloc_context $1 = { secret = 0x69448097523526a7, init_done = 0x1, mmap_counter = 0x0, free_meta_head = 0x0, avail_meta = 0x56042ee901f8, avail_meta_count = 0x59, avail_meta_area_count = 0x0, meta_alloc_shift = 0x0, meta_area_head = 0x56042ee90000, meta_area_tail = 0x56042ee90000, avail_meta_areas = 0x56042ee91000 , active = {0x56042ee901d0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x56042ee901a8, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x56042ee900b8, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x56042ee90090, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x56042ee90068, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x56042ee90040, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x56042ee90018, 0x0 times>}, usage_by_class = {0x1e, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7, 0x0 times>}, unmap_seq = '\000' times>, bounces = '\000' times>, seq = 0x0, brk = 0x56042ee91000 } active = {0x56042ee901d0,0,0...:堆管理器依据申请的size,将chunk分成48类chunk,由sizeclass指定。每类chunk由一个meta结构管理,meta管理的chunk个数有限,由small_cnt_tab指定。当申请个数超出一个meta所能管理的最大数量,堆管理器会再申请同类型meta管理更多的chunk,并且以双向链表结构管理这些相同类型的meta。
usage_by_class = {0x1e, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7,...:表示当前各meta管理着的chunk个数。
secret = 0x69448097523526a7:在meta域每个page大小的首8个byte,都会存在一个校验key。
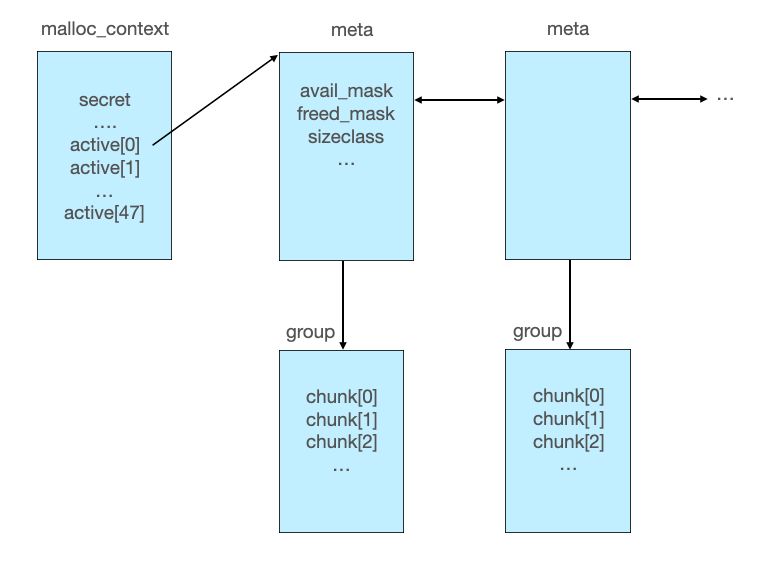
musl libc用以下的结构管理着meta、group以及chunk
分配了两个0x30的chunk,未释放。
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x56042ee901a8 $2 = { prev = 0x56042ee901a8, next = 0x56042ee901a8, mem = 0x7f79e1df5c50, avail_mask = 0x7c, freed_mask = 0x0, last_idx = 0x6, freeable = 0x1, sizeclass = 0x3, maplen = 0x0 } prev和next都指向本身,表示只有一个meta页,meta页由一个双向链表进行维护;
0x7f79e1df5c50是user data域;
avail_mask = 0x7c = 0b1111100表示第0、1个chunk不可用(已经被使用);
freed_mask = 0x0表示没有chunk被释放;
last_idx = 0x6表示最后一个chunk的下标是0x6,总数是0x7个
sizeclass = 0x3表示由0x3这个group进行管理。
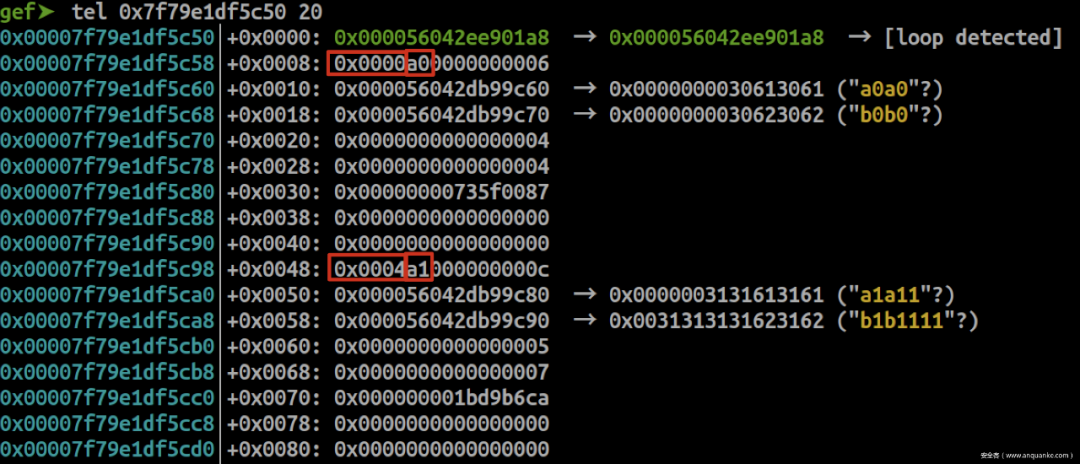
0x000056042ee901a8指向meta结构的地址;
后面8个byte表示chunk的头部结构:
0x0000和0x0001表示当前chunk,距离group首地址0x00007f79e1df5c58的偏移为0和0x40;
0xa0和0xa1表示当前chunk是group中的第0和1个chunk;
再往后0x28个byte就是user data域,最多接收输入0x28+4个byte,占用下一个chunk的前4个byte。
同时,也分配了四个0x10的chunk,未释放
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x56042ee901d0 $3 = { prev = 0x56042ee901d0, next = 0x56042ee901d0, mem = 0x56042db99c50, avail_mask = 0x3ffffff0, freed_mask = 0x0, last_idx = 0x1d, freeable = 0x1, sizeclass = 0x0, maplen = 0x0 } prev和next都指向本身,表示只有一个meta页,meta页由一个双向链表进行维护;
0x56042db99c50是user data域;
avail_mask = 0x3ffffff0 = 0b111111111111111111111111110000表示第0、1、2、3个chunk不可用(已经被使用);
freed_mask = 0x0表示没有chunk被释放;
last_idx = 0x1d表示最后一个chunk的下标是0x1d,总数是0x1e个
sizeclass = 0x3表示由0x3这个group进行管理。
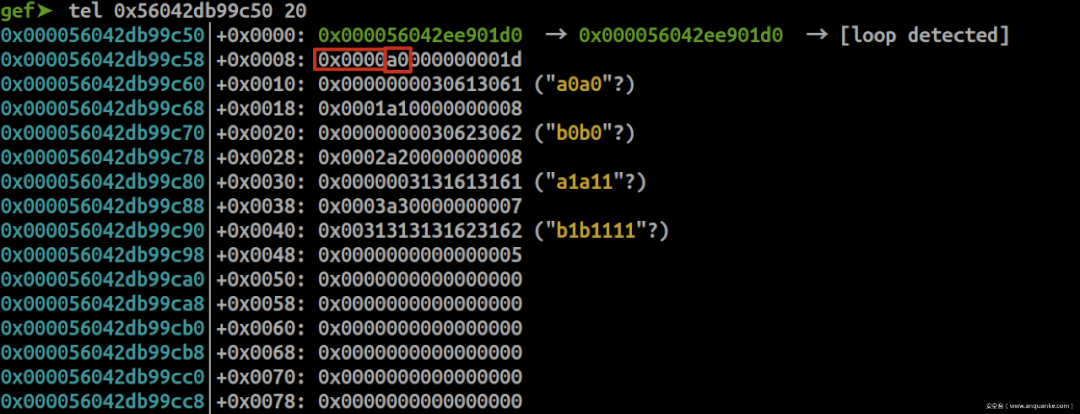
0x0000、0x0001、0x0002、0x0003表示距离group首地址偏移为0、0x10、0x20、0x30byte;
0xa0、0xa1、0xa2、0xa3表示group中的chunk下标;
往后8byte是user data,user data最多接收输入8+4个byte,占用下一个chunk header的前4个byte(与x86的glibc类似)
释放两个0x10的chunk
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x56042ee901d0 $9 = { prev = 0x56042ee901d0, next = 0x56042ee901d0, mem = 0x56042db99c50, avail_mask = 0x3fffffe0, freed_mask = 0x3, last_idx = 0x1d, freeable = 0x1, sizeclass = 0x0, maplen = 0x0 } freed_mask = 0x3 = 0b11表示前两个chunk被释放;
avail_mask = 0x3fffffe0 = 0b111111111111111111111111100000可以发现,此时前两个chunk仍然为不可分配的状态;
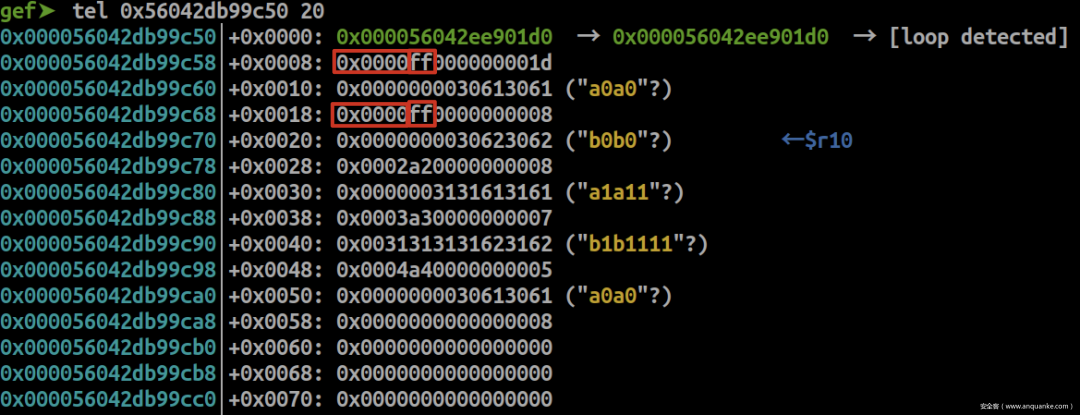
已释放的chunk会将chunk header的offset清零,并且将chunk下标置成0xff,不清空user data域。
释放一个0x30的chunk
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x56042ee901a8 $13 = { prev = 0x56042ee901a8, next = 0x56042ee901a8, mem = 0x7f79e1df5c50, avail_mask = 0x7c, freed_mask = 0x1, last_idx = 0x6, freeable = 0x1, sizeclass = 0x3, maplen = 0x0 } freed_mask = 0x1表示有1个已被释放的chunk。
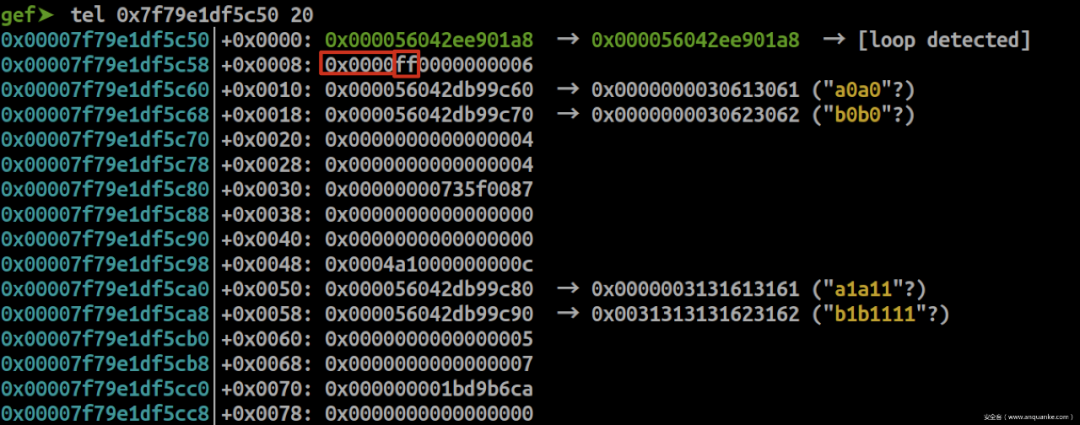
同样,chunk header的offset清零,且chunk下标置0xff。
const uint16_t size_classes[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20, 25, 31, 36, 42, 50, 63, 72, 84, 102, 127, 146, 170, 204, 255, 292, 340, 409, 511, 584, 682, 818, 1023, 1169, 1364, 1637, 2047, 2340, 2730, 3276, 4095, 4680, 5460, 6552, 8191, }; static const uint8_t small_cnt_tab[][3] = { { 30, 30, 30 }, { 31, 15, 15 }, { 20, 10, 10 }, { 31, 15, 7 }, { 25, 12, 6 }, { 21, 10, 5 }, { 18, 8, 4 }, { 31, 15, 7 }, { 28, 14, 6 }, }; static struct meta *alloc_group(int sc, size_t req) { size_t size = UNIT*size_classes[sc]; int i = 0, cnt; unsigned char *p; struct meta *m = alloc_meta();///分配内存,用于建立一个group if (!m) return 0; size_t usage = ctx.usage_by_class[sc]; size_t pagesize = PGSZ; int active_idx; if (sc < 9) { while (i<2 && 4*small_cnt_tab[sc][i] > usage) i++; cnt = small_cnt_tab[sc][i]; } else { ... ctx.usage_by_class[sc] += cnt; ... 几个有用的结构
group分类表,由sc指定由哪个group管理:usage_by_class = {0,0,0,…}
要申请的chunk大小,由这个大小计算出sc:req = 0x30 -> sc = 0x3
malloc的chunk大小:UNITsize_classes = 0x10 0x3 = 0x30
设定该group最多有多少个chunk:ctx.usage_by_class[sc] = 30 = 0x1e
漏洞点(Info Leak)
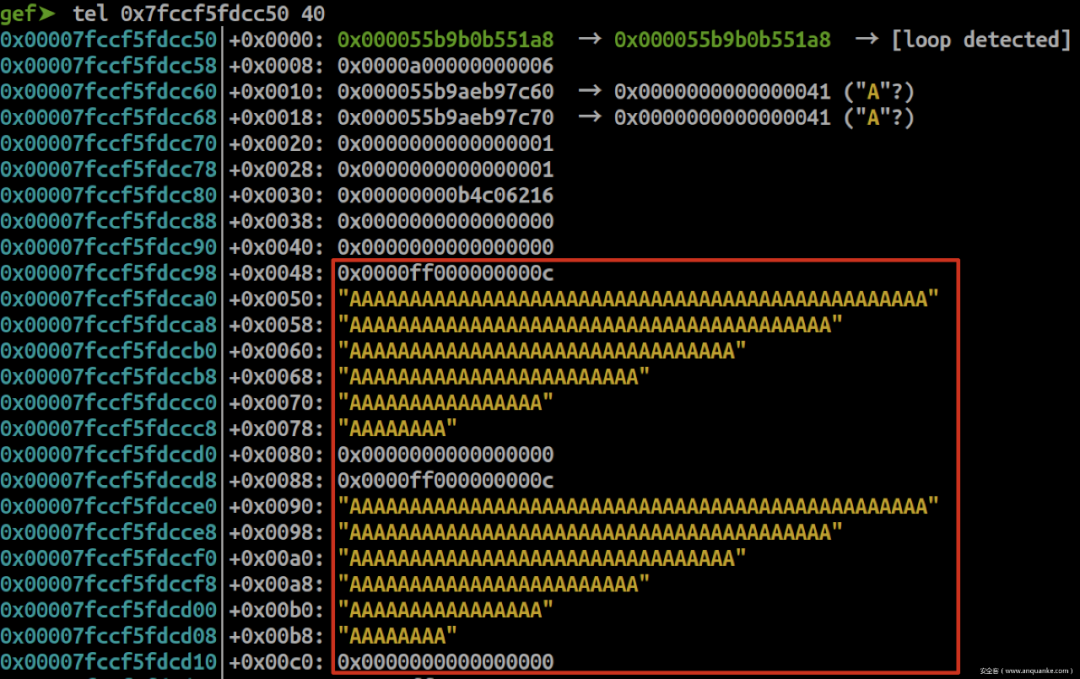
0x30 chunk, malloc 6次,free 5次
store('A', 'A') for _ in range(5): query('A' * 0x30) avail_mask = 0x40 = 0b1000000除了最后一个chunk,其余chunk不可分配;
freed_mask = 0x3e = 0b111110除第一个以及最后一个chunk,其余chunk已被释放
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x55b9b0b551a8 $2 = { prev = 0x55b9b0b551a8, next = 0x55b9b0b551a8, mem = 0x7fccf5fdcc50, avail_mask = 0x40, freed_mask = 0x3e, last_idx = 0x6, freeable = 0x1, sizeclass = 0x3, maplen = 0x0 } 可以发现,free掉的chunk不会优先分配
chunk在被free后不会清空user data域
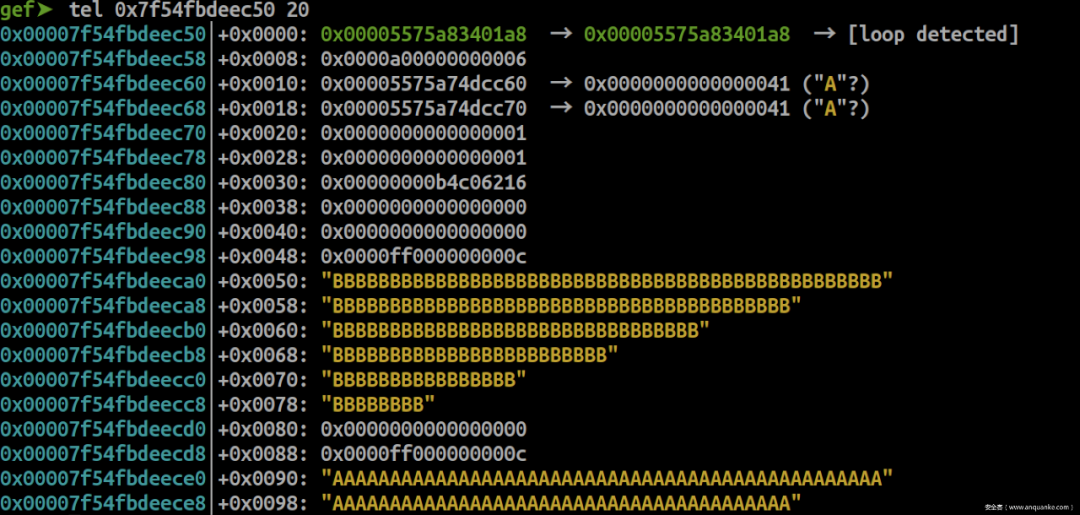
增加到malloc 8次,free 7次
store('A', 'A') for _ in range(5): query('A' * 0x30) query('A' * 0x30) query('B' * 0x30) avail_mask = 0x7c = 0b1111100被释放的chunk重新分配,也就是当耗尽该group的7个chunk时,堆管理器才会检查是否有已被free掉的chunk,将这些chunk的avail_mask置1,再重新分配。
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x5575a83401a8 $2 = { prev = 0x5575a83401a8, next = 0x5575a83401a8, mem = 0x7f54fbdeec50, avail_mask = 0x7c, freed_mask = 0x2, last_idx = 0x6, freeable = 0x1, sizeclass = 0x3, maplen = 0x0 } 现在可以分配回先前已被释放的chunk,这样就有了uaf的利用机会。通过重新将带指针的结构体chunk分配回来,可leak出内存信息。
漏洞点(Hijack)
meta.h
//line:90~100 static inline void dequeue(struct meta **phead, struct meta *m) { if (m->next != m) { m->prev->next = m->next; m->next->prev = m->prev; if (*phead == m) *phead = m->next; } else { *phead = 0; } m->prev = m->next = 0; } 在审计源码时,可以发现这个经典的unsafe-unlink漏洞,跟早期glibc版本unlink宏出现的问题十分类似。
通过伪造fake meta,在删除该meta时,便会产生一次任意写,那么就有了劫持的机会。关于mooosl这道题的完整利用过程会在下篇文章中分析。
转载请注明来自网盾网络安全培训,本文标题:《【技术分享】借助DefCon Quals 2021的mooosl学习musl mallocng(源码审计篇)》










